Relay SDK
The Framework for Stake-Secured Applications
The Symbiotic Relay SDK is the trust layer for data and computation.
It turns any data, computation, or event into money backed, stake secured attestations that settle on chain and trigger programmable outcomes. With Relay you:
- Reduce and keep costs constant at scale. Validator-set verification uses BLS aggregation and optional ZK compression to keep EVM verify gas essentially flat, regardless of validator set size.
- Put capital behind data. Every attestation is secured by stake and can be subject to slashing.
- Reduce integration friction. One standardized attestation flow replaces bespoke oracles and middleware.
- Automate across chains. Verify once, then mint, swap, bridge, update feeds, or call adapters anywhere.
Relay is the missing link between computation and consensus, the universal economically secured proof layer for the modular internet.
The Problem that Relay Solves
Large validator sets became prohibitively expensive to verify across chains. Networks with hundreds of operators were facing millions per year in verification costs on Ethereum alone. At the same time, protocols that wanted to run multichain were pushed into Proof-of-Authority models because staking data was not available cross-chain in a usable, verifiable way.
How it Works
-
Application Layer
Any app or service performs a task: fetching prices, running an AI model, or monitoring transactions.
-
Relay Network
Operators in the Relay Network generate cryptographic attestations that confirm the task was executed as claimed.
-
Relay Settlement
These attestations are verified on-chain using validator stakes within Symbiotic Core contracts.
-
On-Chain Action
Once verified, the attestation can trigger any programmable outcome:
- Mint a token
- Update a price feed
- Trigger a bridge transaction
- Perform a swap
- Feed data into a DeFi protocol
Key Value Proposition
The Relay turns any external workload into a verifiable on-chain action. Networks plug in a lightweight client, inherit stake-backed security with slashing, and use a single attestation flow that works across chains and use cases. The result is less code to maintain, clearer guarantees, and a portable integration you can reuse everywhere.
Relay Advantages
- Cheaper at scale Validator-set verification uses BLS aggregation (and optional ZK compression) to keep EVM verification costs essentially constant, independent of validator count. This removes the linear cost curve that made large decentralized sets impractical.
- Ship faster Replace bespoke middleware with a small client + SDK. Fewer contracts to write and audit → shorter path to mainnet.
- Cross-chain by default Verify and trigger outcomes on any EVM; plug into Hyperlane/DVN/others through adapters.
- Stronger guarantees Attestations are backed by staked validators with slashing. You inherit economic security instead of trusting a vendor or multisig.
- Unified interface One attestation format for any workload (AI, compute, data, bridge ops). No new pipeline per use case.
- Smaller attack surface Less custom glue code, fewer moving pieces, clearer trust model.
- Deterministic programmability Attestations can mint, swap, bridge, update feeds, call adapters → compose like Lego across verticals.
- Cost predictability Pay for attestation + on-chain verify; avoid standing infra and surprise ops costs.
- Vendor neutrality Bring your own operators/curators, swap them out, or add more. No lock-in.
Relay Features
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Universal Attestation Framework | Any data, any computation, any chain → one system for proof generation |
| Verifiable On-Chain | Proofs backed by staked validators, ensuring economic security |
| Fully Modular SDK | Developers integrate using lightweight clients in Go, Rust, or TypeScript |
| Chain-Agnostic | Works across L1s, L2s, and rollups; interoperable with all EVMs. Cosmos integration is available out of the box through a dedicated SDK. |
| Programmable & Application-Agnostic | Plugs into any smart contract workflow; attestations act as a generic trigger for programmable outcomes. |
System Architecture
Every operator runs:
- A Relay Sidecar → connects to other relay nodes via a p2p network
- An Application Node → runs arbitrary code (AI, oracle, bridge, etc.) and communicates with the Sidecar through an API
Together, these produce verifiable proofs of arbitrary work, enabling on-chain action triggers and outcome settlement.
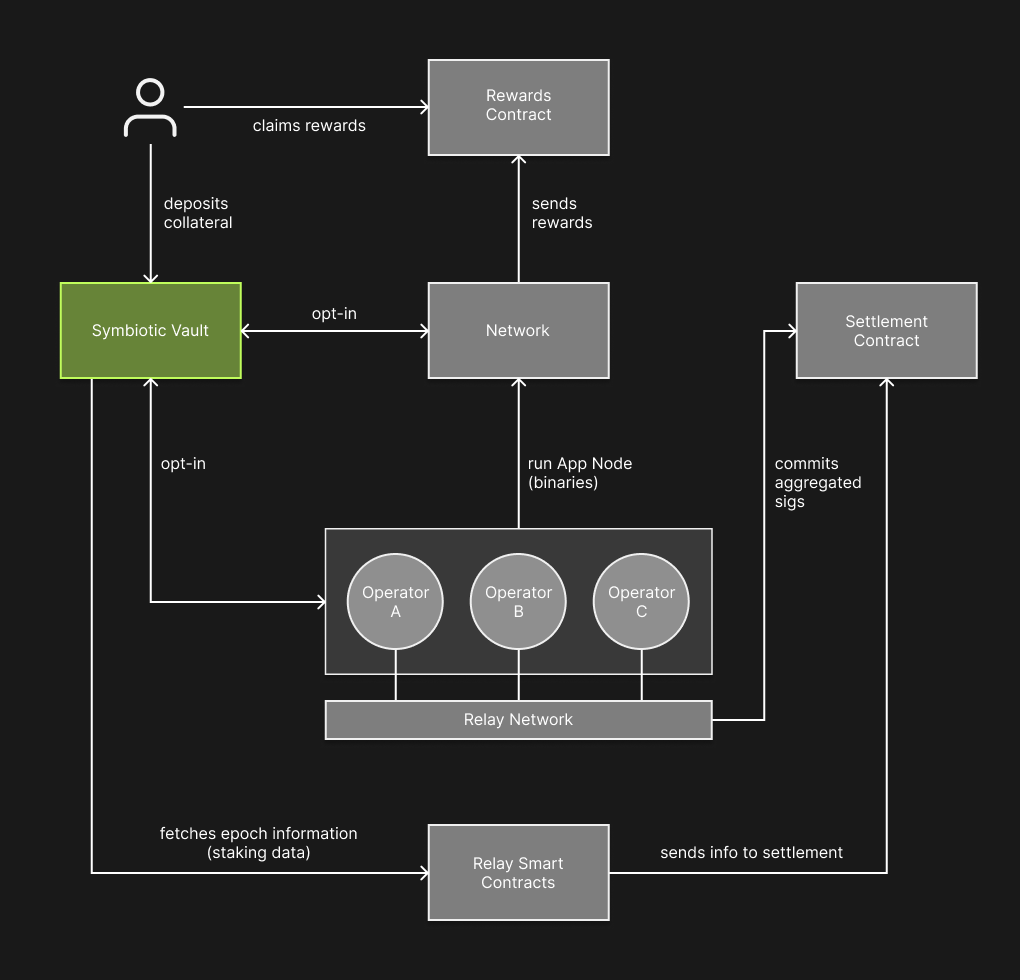
How Relay Integrates with Symbiotic
Relay plugs into Symbiotic Vaults out of the box, so networks can adopt it immediately and still customize everything, including validator sets, quorum thresholds, collateral, and reward logic. The Relay contracts read staking state from the vaults each epoch to see who the active operators are and how much voting power they have.
The settlement contract receives this data, verifies the attestations, and then triggers the onchain outcome.


